
个人信息
Personal Information
联系方式
Contact Information
个人简介
Personal Profile
本人主要从事城市水文、极端暴雨洪水事件、机器学习预测模拟等研究。“育人先育心,育心先自育”,期待与亲爱的同学们平等交流、自由互动、深度对话,师生融乐,共同进步。
欢迎报考硕士研究生。
有关论文情况可见网页:https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Zhengzheng-Zhou-2

上海短历时暴雨风险变化图
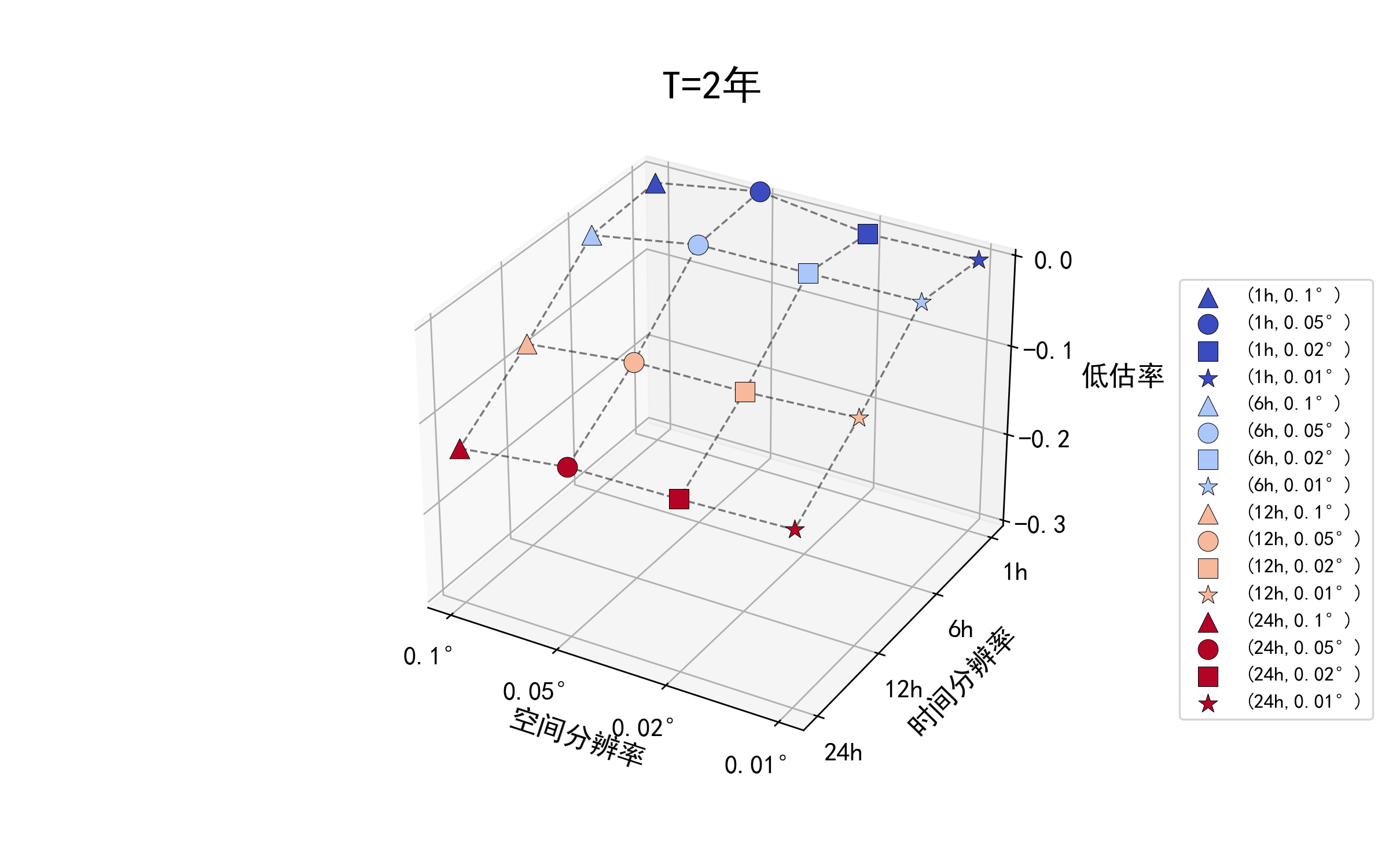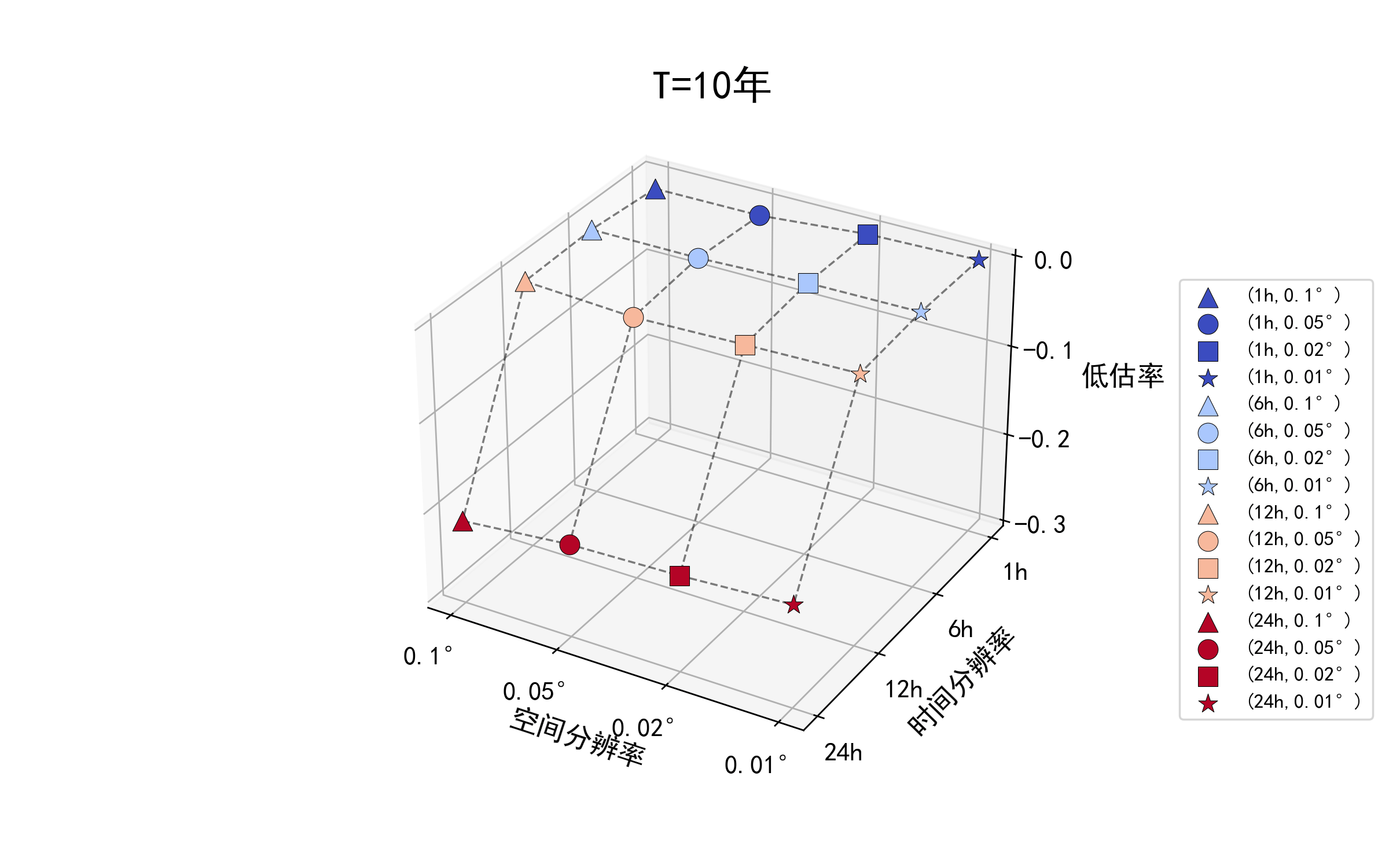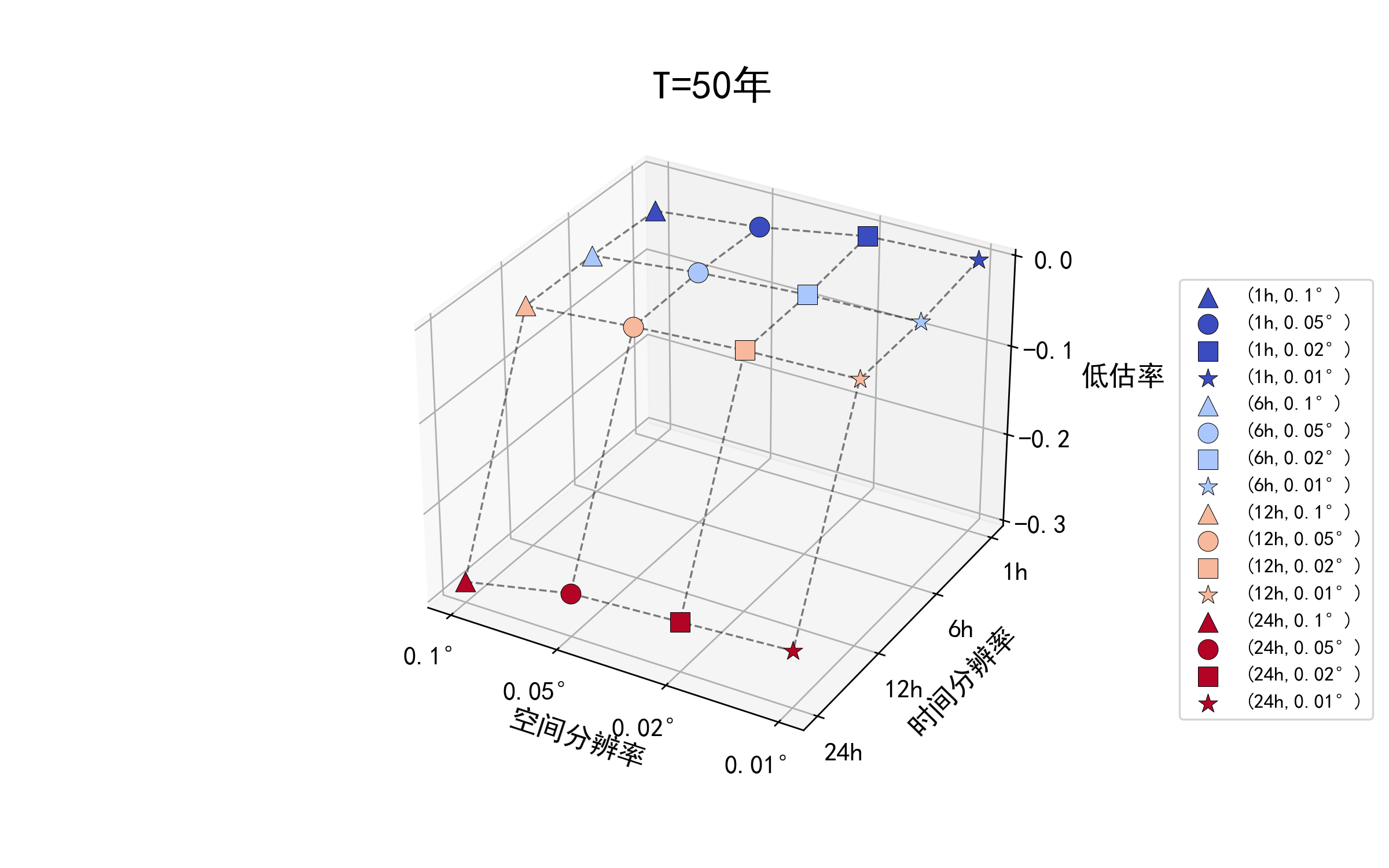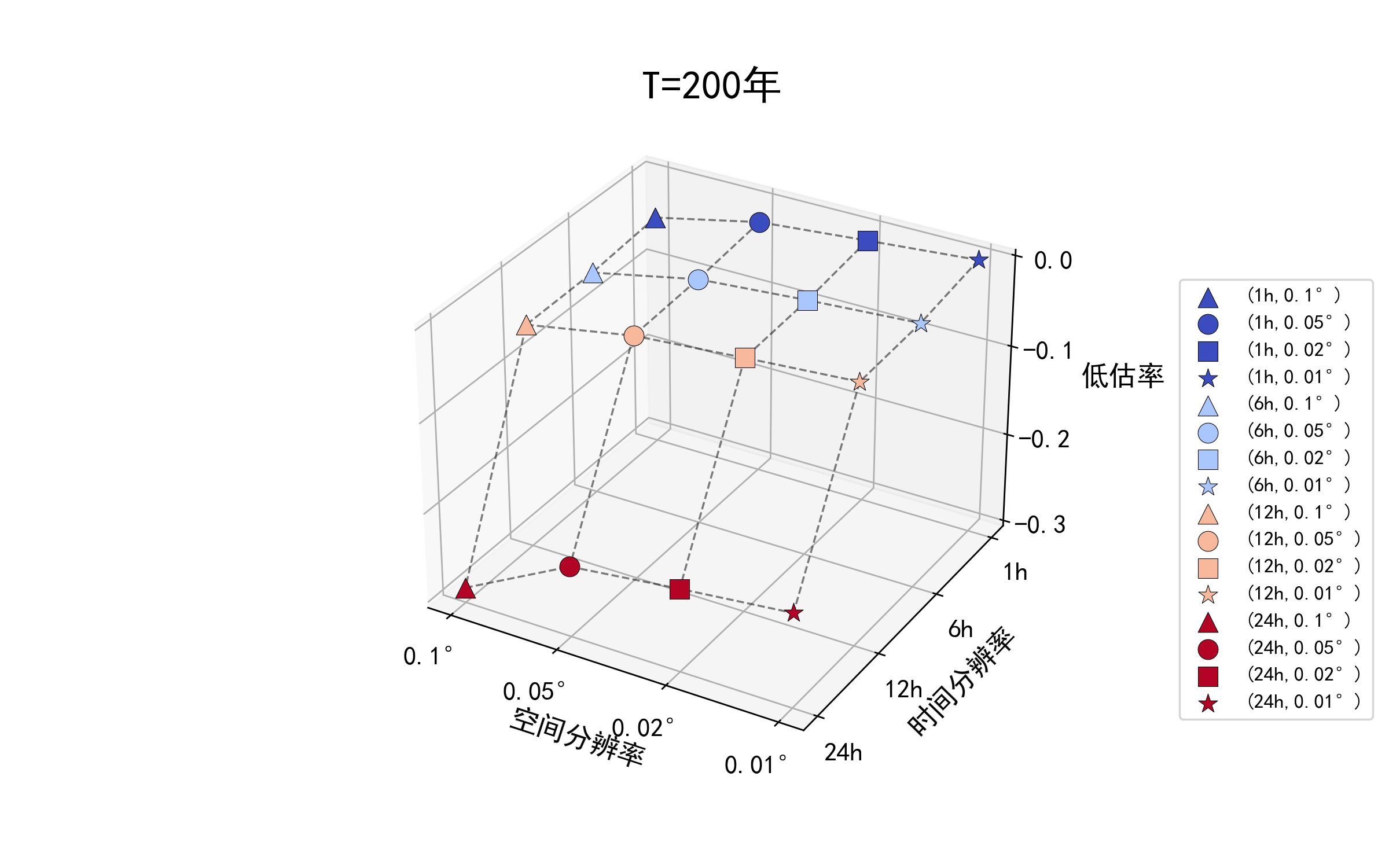
不同重现期下的降雨数据时空精度对设计暴雨结果的影响

国家自然科学基金面上基金,《气候变化条件下超大城市暴雨时空变异性及其对洪水的影响机理》,2024-2027.
上海市海洋局科研项目,《极端高温和干旱条件下上海市沿江沿海夏季径流量变化及其与咸潮入侵相关关系研究》,2023.
国家自然科学基金青年项目, 暴雨空间分布不均匀性对城市洪水响应的影响机制研究, 2020.01-2022.12.
国家自然科学基金国际(地区)合作与交流项目,中俄大型城市暴雨时空变异性及其对径流水质的影响对比研究,2021-2022.
中国博士后科学基金面上一等资助,考虑降雨空间分布结构的城市流域设计暴雨研究,2018-2019.
国家自然科学基金面上基金,《气候变化条件下超大城市暴雨时空变异性及其对洪水的影响机理》,2024-2027.
上海市海洋局科研项目,《极端高温和干旱条件下上海市沿江沿海夏季径流量变化及其与咸潮入侵相关关系研究》,2023.
国家自然科学基金青年项目, 暴雨空间分布不均匀性对城市洪水响应的影响机制研究, 2020.01-2022.12.
国家自然科学基金国际(地区)合作与交流项目,中俄大型城市暴雨时空变异性及其对径流水质的影响对比研究,2021-2022.
中国博士后科学基金面上一等资助,考虑降雨空间分布结构的城市流域设计暴雨研究,2018-2019.
出版专著:
《典型流域、区域与城市的设计暴雨研究》,刘曙光,周正正,韩超,梁玉音,同济大学出版社,2023.
学术论文:
Lei, N., Gao, L., Liu, S., Zhou, Z.*, 2024. The Spatiotemporal Clustering of Short‐Duration Rainstorms in Shanghai City Using a Sub‐Hourly Gauge Network. Earth and Space Science, 2024, 11(3): e2023EA003442.
Liang, J., S. Liu, Z. Zhou*, G. Zhong, and Y. Zhen: Improving probabilistic streamflow predictions through a nonparametric residual error model, Environmental Modelling & Software, 2024, 175, 105981.
庄琦,刘曙光,周正正*. 降雨数据时空精度对城市暴雨变异性及频率分析的影响[J]. 水科学进展, 2023, 34(3): 398-408.
Lei N., Zhou Z.*, Zhuang Q., Chen W., Chalov S.R., Liu S.,Gao L.,Dong G. Performance Evaluation and Improvement of CMFD's Precipitation Products Over Shanghai City, China[J]. Earth and Space Science, 2023, 10(3): e2022EA002690.
Zhuang Q.,Zhou Z.*, Liu S., Wright D.B., Gao L. The evaluation and downscaling-calibration of IMERG precipitation products at sub-daily scales over a metropolitan region[J]. Journal of Flood Risk Management, 2023, e12902.
Zhuang, Q., Zhou Z*, Liu, S., et. al. Bivariate Rainfall Frequency Analysis in an Urban Watershed: Combining Copula Theory with Stochastic Storm Transposition. Journal of Hydrology, 2022, 615: 128648.
Liu S, Zheng W, Zhou, Z.*, Zhong G, Zhen Y, Shi Z. Flood Risk Assessment of Buildings Based on Vulnerability Curve: A Case Study in Anji County. Water. 2022; 14(21):3572.
Zhen, Y., Liu, S., Zhong, G., Zhou, Z.*, Liang, J., Zheng, W., & Fang, Q. Risk assessment of flash flood to buildings using an indicator-based methodology: A Case study of mountainous rural settlements in Southwest China. Frontiers in Environmental Science, 2022, 10:931029.
Gu, J., Liu, S., Zhou, Z.*, Chalov, S. R., Zhuang, Q.. A Stacking Ensemble Learning Model for Monthly Rainfall Prediction in the Taihu Basin, China. Water, 2022, 14(3): 492.
Zhou, Z.*, Ren J., He, X., Liu, S. A comparative study of extensive machine learning models for predicting long‐term monthly rainfall with an ensemble of climatic and meteorological predictors. Hydrological processes, 2021;35:e14424.
Zhou, Z.*, Smith, J.A., Baeck, M.L., Wright, D.B., Smith, B.K., Liu S. The impact of the spatiotemporal structure of rainfall on flood frequency over a small urban watershed: an approach coupling stochastic storm transposition and hydrologic modeling. Hydrology and Earth System Science, 2021, 25(8): 4701-4717.
Zhuang, Q., Liu S., Zhou Z*. Spatial Heterogeneity Analysis of Short-Duration Extreme Rainfall Events in Megacities in China. Water, 2020, 12(12), 3364.
Hu, Z., Liu, S., Zhong, G., Lin, H., Zhou, Z. Modified Mann-Kendall trend test for hydrological time series under the scaling hypothesis and its application. Hydrological Sciences Journal, 2020,65(14): 2419-2438.
周正正; 刘曙光; Daniel B. Wright ; 基于随机暴雨移置方法的城市设计暴雨分析, 水科学进展, 2020, 31(4): 583-591
Zhou, Z. *, Smith, J.A., Wright, D.B., Baeck, M.L., Yang, L., and Liu, S. Storm catalog-based analysis of rainfall heterogeneity and frequency in a complex terrain. Water Resources Research, 2018, 55(3), 1871-1889
Ten Veldhuis, M.-C.*, Zhou, Z.*, Yang, L., Liu, S., and Smith, J. The role of storm scale, position and movement in controlling urban flood response. Hydrology and Earth System Science, 2018, 22(1), 417-436.
Zhou, Z. *, Smith, J.A., Yang, L., Baeck, M.L., Chaney, M., Ten Veldhuis, M.C., Deng, H. and Liu, S. The complexities of urban flood response: Flood frequency analyses for the Charlotte Metropolitan Region. Water Resources Research, 2017, 53(8), 7401-7425
Zhou, Z., Liu, S., Hu, Y., Liang, Y., Lin, H. and Guo, Y. Analysis of precipitation extremes in the Taihu Basin of China based on the regional L-moment method. Hydrology Research, 2016, 48(2), 468-479
Zhou, Z., Liu, S., Zhong, G. and Cai, Y. Flood disaster and flood control measurements in Shanghai. Natural Hazards Review, 2017, 18(1), p.B5016001
Zhou, Z., Liu, S., Hua, H., Chen, C.S., Zhong, G., Lin, H. and Huang, C.W. Frequency analysis for predicting extreme precipitation in Changxing station of Taihu Basin, China. Journal of Coastal Research, 2014, 68(sp1), 144-151
Zhang, X., Hu Y., Liu, S., Zhong, G., Zhou, Z. A comparison of parameter estimation methods using typical precipitation data in palin river networks: case study in Taihu Basin, China. Proceedings of the 26th International Ocean and Polar Engineering Conference. Rhodes, Greece, June 26-July1, 2016. ISOPE, 2016, 792-797.
梁玉音, 刘曙光, 钟桂辉, 周正正, & 胡艳 (2013). 线性矩法与常规矩法对太湖流域降雨频率分析的比较研究. 水文, 33(4), 16-21.
Zhuang Q.,Zhou Z.*, Liu S., Wright D.B., Gao L. The evaluation and downscaling-calibration of IMERG precipitation products at sub-daily scales over a metropolitan region[J]. Journal of Flood Risk Management, 2023, e12902.
Zhuang, Q., Zhou Z*, Liu, S., et. al. Bivariate Rainfall Frequency Analysis in an Urban Watershed: Combining Copula Theory with Stochastic Storm Transposition. Journal of Hydrology, 2022, 615: 128648.
Liu S, Zheng W, Zhou, Z.*, Zhong G, Zhen Y, Shi Z. Flood Risk Assessment of Buildings Based on Vulnerability Curve: A Case Study in Anji County. Water. 2022; 14(21):3572.
Zhen, Y., Liu, S., Zhong, G., Zhou, Z.*, Liang, J., Zheng, W., & Fang, Q. Risk assessment of flash flood to buildings using an indicator-based methodology: A Case study of mountainous rural settlements in Southwest China. Frontiers in Environmental Science, 2022, 10:931029.
Gu, J., Liu, S., Zhou, Z.*, Chalov, S. R., Zhuang, Q.. A Stacking Ensemble Learning Model for Monthly Rainfall Prediction in the Taihu Basin, China. Water, 2022, 14(3): 492.
Zhou, Z.*, Ren J., He, X., Liu, S. A comparative study of extensive machine learning models for predicting long‐term monthly rainfall with an ensemble of climatic and meteorological predictors. Hydrological processes, 2021;35:e14424.
Zhou, Z.*, Smith, J.A., Baeck, M.L., Wright, D.B., Smith, B.K., Liu S. The impact of the spatiotemporal structure of rainfall on flood frequency over a small urban watershed: an approach coupling stochastic storm transposition and hydrologic modeling. Hydrology and Earth System Science, 2021, 25(8): 4701-4717.
Zhuang, Q., Liu S., Zhou Z*. Spatial Heterogeneity Analysis of Short-Duration Extreme Rainfall Events in Megacities in China. Water, 2020, 12(12), 3364.
Hu, Z., Liu, S., Zhong, G., Lin, H., Zhou, Z. Modified Mann-Kendall trend test for hydrological time series under the scaling hypothesis and its application. Hydrological Sciences Journal, 2020,65(14): 2419-2438.
周正正; 刘曙光; Daniel B. Wright ; 基于随机暴雨移置方法的城市设计暴雨分析, 水科学进展, 2020, 31(4): 583-591
Zhou, Z. *, Smith, J.A., Wright, D.B., Baeck, M.L., Yang, L., and Liu, S. Storm catalog-based analysis of rainfall heterogeneity and frequency in a complex terrain. Water Resources Research, 2018, 55(3), 1871-1889
Ten Veldhuis, M.-C.*, Zhou, Z.*, Yang, L., Liu, S., and Smith, J. The role of storm scale, position and movement in controlling urban flood response. Hydrology and Earth System Science, 2018, 22(1), 417-436.
Zhou, Z. *, Smith, J.A., Yang, L., Baeck, M.L., Chaney, M., Ten Veldhuis, M.C., Deng, H. and Liu, S. The complexities of urban flood response: Flood frequency analyses for the Charlotte Metropolitan Region. Water Resources Research, 2017, 53(8), 7401-7425
Zhou, Z., Liu, S., Hu, Y., Liang, Y., Lin, H. and Guo, Y. Analysis of precipitation extremes in the Taihu Basin of China based on the regional L-moment method. Hydrology Research, 2016, 48(2), 468-479
Zhou, Z., Liu, S., Zhong, G. and Cai, Y. Flood disaster and flood control measurements in Shanghai. Natural Hazards Review, 2017, 18(1), p.B5016001
Zhou, Z., Liu, S., Hua, H., Chen, C.S., Zhong, G., Lin, H. and Huang, C.W. Frequency analysis for predicting extreme precipitation in Changxing station of Taihu Basin, China. Journal of Coastal Research, 2014, 68(sp1), 144-151
Zhang, X., Hu Y., Liu, S., Zhong, G., Zhou, Z. A comparison of parameter estimation methods using typical precipitation data in palin river networks: case study in Taihu Basin, China. Proceedings of the 26th International Ocean and Polar Engineering Conference. Rhodes, Greece, June 26-July1, 2016. ISOPE, 2016, 792-797.
梁玉音, 刘曙光, 钟桂辉, 周正正, & 胡艳 (2013). 线性矩法与常规矩法对太湖流域降雨频率分析的比较研究. 水文, 33(4), 16-21.

文件上传中...